What Does the Latent Heat of Vaporization Represent
The energy absorbed in this process is called heat of vaporization. The vaporization is the opposite process of condensation.

Want To Unlock The Mystery Surrounding The Properties Of Air Then Check Out Our Post On The Psychrometric Chart Diy และงานฝ ม อ
Latent comes from the Latin latere which means to lie hidden or concealed.

. The heat of fusion for water at 0 C is approximately 334 joules 797 calories per gram and the heat of vaporization at 100 C is about 2230 joules 533 calories per gram. The energy needed to completely vaporize a mole of a liquid. The latent heat of vaporization is what.
Does heat of vaporization change with temperature. In the process of heat conduction thermal energy is usually transferred from fast moving particles to slow moving particles during the collision of these particles. It neither goes up nor down.
Latent heat of vaporization Latent heat of vaporization is the heat consumed or discharged when matter disintegrates changing stage from fluid to gas stage at a consistent temperature. HEAT OF VAPORIZATION used as a noun is very rare. When a material in liquid state is given energy it changes its phase from liquid to vapor.
Heat absorbed by a unit mass of a material at its boiling point in order to convert the material into a gas at the same temperature. What does it mean by latent heat of vaporization of water 2256 x 106Jkg. In the formulas for latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization what does Q represent.
It is measured in Joules per mole Jmol or sometimes in Calories C. Latent heat is the type of energy absorbed or released that changes the state of a body without affecting its temperature. The heat of vaporization of water is about 2260 kJkg which is equal to 408 kJmol.
Latent heat of vaporization is the heat consumed or discharged when matter disintegrates changing state from fluid to gas state at a consistent temperature. The heat of vaporization is a latent heat. Q represents the quantity of heat energy transferred for the phase change.
The energy needed to heat a liquid from freezing point to boiling point O D. Note that some molecules of water ones that happen to have high kinetic energy will escape from the surface of the water even. What is meant by latent heat of ice.
The heat of condensation is defined as the heat released when one mole of the substance condenses at its boiling point under standard pressure. J also known as the latent heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation. Latent heat is the additional heat required to change the state of a substance from solid to liquid at.
It is the quantity of heat energy released or absorbed during the change of phase of a. You started pouring 15C water over it. The amount of energy required to turn a mole of a liquid into a gas What is the latent of vaporization.
The amount of heat released or absorbed by a substance the mass of a substance the amount of a substance that changes state the temperature of a substance 2 See answers Advertisement carolmartelotte2020 Answer. Latent heat of vaporization. In the formulas for latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization Q represents the amount of heat of energy released or absorbed by a substance.
What information does the latent heat of vaporization give. What does the latent heat of vaporization represent. The units are calgram and values for the heat of vaporization of water at different temperatures are given in Table 31.
For example when 03 kilograms of alcohol is evaporating it absorbs 2565 kJ of heat. The temperature of the body remains constant throughout this whole process. Vaporization and fusion are.
The heat required to change 1 g of a liquid at its boiling point to vapor at the same temperature. The heat of vaporization of water is about 2260 kJkg which is equal to 408 kJmol. In this case Q is the amount of heat absorbed m represents the mass of substance which will evaporate and H v is the specific latent heat of vaporization of the substance.
This energy breaks down the intermolecular attractive forces. Heat of Vaporization Explained. Heat of Vaporization Definition Also known as enthalpy of vaporization the heat of vaporization H vap is defined by the amount of enthalpy heat energy that is required to transform a liquid substance into a gas or vapor.
What is the heat of evaporation of wateraround 540 calgHeat of vaporization of water Waters heat of vaporization is around 540 calg at 100 C waters boiling point. The enthalpy of vaporization ΔHv is additionally named the. Latent heat of vaporization is a physical property of a substance.
You are trying to cool a 12 kg piece of iron which you heated initially at 650C. QUIZ QUIZ YOURSELF ON HAS VS. In case of liquid to gas phase change this amount of energy is known as the enthalpy of vaporization symbol H vap.
In order to understand the temperature heat and thermal equilibrium you are planning to do an interesting experiment in the lab. The latent heat of vaporization is the latent heat involving a liquid that forms a gas or vice versaLatent means hidden or unseen. The heat of vaporization of water is the most elevated known.
Heat of vaporization is the quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g of it to be converted from the liquid to the. The Q in the formula Q m x L represents the quantity of heat required to totally effect a phase change of a unit of mass m usually 1kg of a substance. The energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of a vapor 1C O c.
Latent heat is the amount of heat added to or removed from a substance to produce a change in phase. The energy needed to completely melt a mole of a solid B.
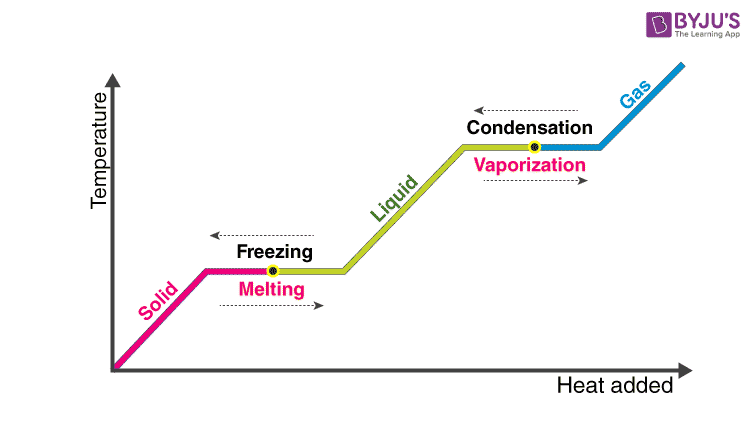
Latent Heat Definition Types Formula Fusion And Vaporization

Psychrometric Chart Warm Air Is More Humid Than Cool Air Gif Psychrometric Chart Water From Air Chart
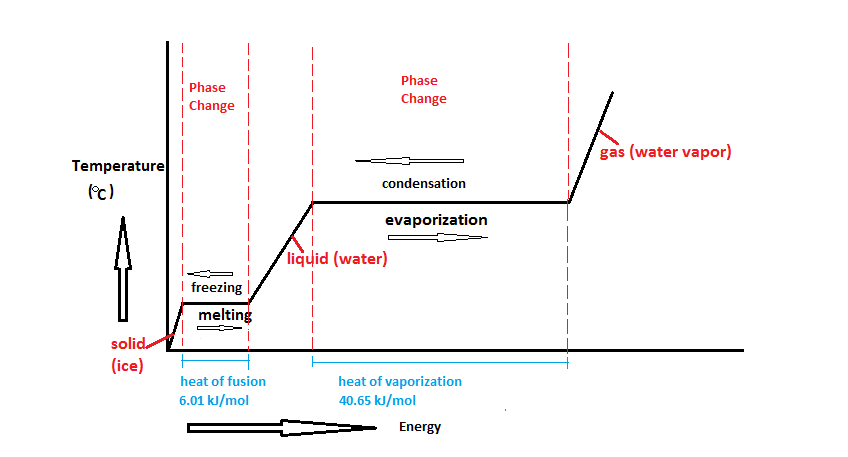
Comments
Post a Comment